
Mammals Around Las Vegas, Wildlife Around Las Vegas
 Typical Coyote: scrawny little puppy |
Identification: Coyotes (Canis latrans) are medium sized dogs with a long snout and a tail that is bushier than most domestic dogs. In the western deserts, they are usually tan or reddish with some black above and white below. Coyotes run with their tail held low behind their legs, which is in contrast to foxes that run with the tail held straight out. Coyote eyeshine is greenish-gold. Diet: Coyotes eat anything that doesn't run faster than they do, but their diet mainly consists of ground squirrels, rabbits, carrion (the meat of dead animals), and plant matter. Their scat usually contains a few bone fragments, hair, and berries, seeds, or grass. Coyotes are social creatures, usually living in packs. They often hunt socially, with members of the pack spreading out to scare up a rabbit, and then individuals taking turns running the rabbit until the animal is exhausted and caught. |
 A well-fed Coyote |
Coyote scat: The actual size is about 4-inches long. Coyotes eat as much meat as they can, so you can usually find fur and bits of bone in the scat. Coyotes also eat lots of berries, so it is not uncommon to find a scat full of juniper berries or mesquite beans. Coyotes are subject to much legend and lore, but the fierce nature attributed to these little dogs is all hype (unless you are a ground squirrel or rabbit). While urban coyotes can become a problem, wild coyotes in the desert do not attack people. While the singing of a pack of coyotes brings shudders to some people, I think the sound of a pack singing is one of the most amazing wonders of the nighttime desert. |
 |
Coyote and Kit Fox tracks in a dusty dirt road. Coyote tracks are large and oval, while Kit Fox tracks are small and round. |
 |
Coyote tracks in the mud. The impression of the toe and heal pads are similar to those of wild cats (e.g., mountain lion, bobcat), but note that the claw marks show clearly in the mud. Cats retract the claws, so they do not show in mud tracks. |
 |
Coyote den with collapsed entrance tunnel. Coyotes dig dens in soft dirt. Because the entrance of this tunnel has collapsed, we can see how coyote burrows usually run straight for a few feet, then curve to the side. Although not the case here, coyote burrows often drop at a steep angle. The entrance always seems too small for a coyote, but they can fit in amazingly small holes. |
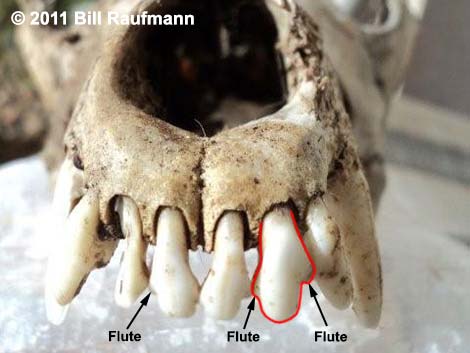 |
Hikers sometimes find skulls in the desert, but identifying skulls can be difficult. To determine if a skull is from a dog (coyote, kit fox, or domestic dogs), check the incisors (the teeth at the front of the mouth). Coyotes and other dogs have fluted incisors, making it easy to identify a dog skull. |
 |
Coyote skulls differ from most other dogs by the length (long), shape (narrow), clearly separating coyotes from kit foxes (much smaller), small domestic dogs (smaller), and short-nosed domestic dogs (e.g., pit bulls). From shepherds and other large, long-nosed dogs, coyotes have longer canine teeth. |
 |
If you were a tasty bunny or perhaps a yummy mesquite seedpod, this might be the last face you ever see! |
 Healthy Coyote |
 Coyote begging |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 Coyote scat after eating manzanita berries |
 Scat with manzanita berries |
 Coyote barf - undigested cactus apples |
 Coyote poop - digested cactus apples |
 Big, healthy scat |
 Dry, but relatively fresh scat after eating lots of mammal meat |
 Older coyote scat after eating small rodents |
 Coyote scat with mesquite seeds |
 Coyote burrow; notice large hole, large stones, and steep dirt pile |
 Coyote burrow; notice steep entrance and turn to the left |
 Coyote burrow |
 Coyote burrow |
 |
 |
 Coyote begging on road in Death Valley; this is not good |
 Coyote |
Note: All distances, elevations, and other facts are approximate.
![]() ; Last updated 230917
; Last updated 230917
| Mammals Around Las Vegas | Wildlife Around Las Vegas | Glossary | Copyright, Conditions, Disclaimer | Home |