
Mammals Around Las Vegas, Wildlife Around Las Vegas
 |
General Information: Kit Foxes (Vulpes macrotis) are small dogs with over-sized ears and a long, fluffy tail with a black tip. Overall, the color is gray on the back and tail, and reddish on the face, belly, and legs. Kit Foxes can be confused with Gray Foxes. Gray Foxes, however, are larger, have more-normal sized dog ears, and they have a black stripe along the top of the tail. Taxonomy: Order: Carnivora; Family: Canidae. |
 |
Technical Description: Breeding: Mates in the spring; raises young into the summer. Diet: Eats bugs, mice, and other small creatures. Range: Kit Foxes occur throughout lower-elevation arid areas in the western US from the Great Plains in southern Canada south into Mexico. |
 |
Kit Fox burrows often occur in clusters. Here, a large area is affected by their digging, and there are several burrows or burrow entrances. |
 |
Kit fox burrow. Notice the near-vertical sides and a tunnel that curves to the side. Compare this with desert tortoise burrows, which have sloping sides and usually are straight. |
 |
Kit fox tracks in mud. Notice the small, round feet that are well haired on the bottom. Kit fox claws often do not show in the track, but in this case, they do show. |
 |
Kit fox track (right) adjacent to Coyote (Canis latrans) track (left). Notice that the kit fox track is smaller and more round than the coyote track. |
 |
Kit fox scat. Notice the several pieces, irregular shapes, and presence of hair from the prey items. If this were broken open, it likely would reveal chewed up bones from small mammals. In contrast, Coyote scat often is one large log with more regular shape. |
 Kit fox warren with several entrances |
 Notice the large amount of dirt moved |
 Notice the large amount of dirt moved and vertical walls |
 Dog burrows often angle down steeply |
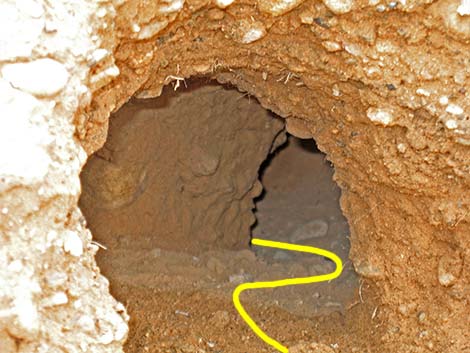 Note the near-vertical walls and crooked tunnel |
 Note the near-vertical walls and curved tunnel |
 Kit fox tracks in the mud |
 Kit fox tracks in the mud |
 Track in mud, notice that claws marks sometimes do not show |
 Track in soft mud showing claw marks |
 Scat |
 Latrine atop rock atop knoll |
 This latrine has been used for a long time |
 This latrine has been used for a long time |
 |
 |
 Kit Fox latrine |
 Kit Fox latrine |
 Kit Fox scat at latrine |
 Kit Fox scat at latrine |
| Mammals Around Las Vegas | Wildlife Around Las Vegas | Glossary | Copyright, Conditions, Disclaimer | Home |