
Annual Forbs Around Las Vegas, Vegetation Around Las Vegas
 Stiff, branching forb |
General: African Mustard (Strigosella africana) is a short, stiff-stemmed upright annual forb with many basal leaves and branched flowering stalks. All parts of the plant are stiff and covered with tiny, forked hairs. The basal leaves are elongate and covered with tiny bumps, and each bump has a hair. Upper leaves are reduced. The flowers are violet to pink with four petals. Fruits are linear and held up and away from the stem. The plant dies after it flowers, leaving open, upright stalks that promote wildfire. African Mustard is an uncommon component of disturbed desert vegetation communities. Around Las Vegas, look for this species in town and in disturbed roadsides and open fields in the desert. This is an invasive weed. If hikers and other visitors to the native habitats around Las Vegas see this species, please try to pull it out. If you have this species on your private property, please eradicate it. |
 Purple flowers |
Family: Mustard (Brassicaceae). Other Names: Malcolmia africana. Plant Form: Basal leaves with upright flower stalks, stiff. Height: To about 18 inches. Stems: Branched, hairs. Leaves: Basal leaves are elongate and covered with hairs, some forked. Flowers: Blooms during early spring. Flowers clustered at the top of the flower stalks, but the stalks continue to grow past the flower; petals 4, violet to pink. Fruits are erect, usually held away from the stem; to about 2-inches long. |
 Basal leaves are elongate and covered with hairs, some forked |
Seeds: Tiny, many per plant. Habitat: Roadsides, fields, disturbed sites. Elevation: About 4,000 to 6,000 feet. Distribution: Throughout the western US and southern Canada; native to the Mediterranean region. Comments: Like Sahara Mustard, African Mustard is adapted to fire and increases the fuel load available for fires, thus contributing to the conversion of native desert vegetation to an open grassland. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 Leaf surface is bumpy, and each bump has a forked hair |
 Leaf surface is bumpy, and each bump has a forked hair |
 |
 |
 Developing purple flowers |
 Developing purple flowers and stems with hairs |
 Flower: purple with 4 petals |
 Flower: purple with 4 petals |
 Flower: purple with 4 petals |
 Flower: purple with 4 petals |
 Fruits develop as the plant puts on new flowers |
 Hairs on a fruit |
 The skeletons of dead plants persist |
 Dried lives remain stiff and covered with hairs |
 Single stem with fruits |
 Single fruit |
 Hairs on a fresh fruit. Hairs are similar on the rest of the plant |
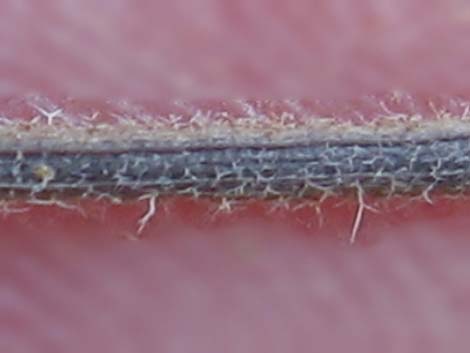 Hairs on a dried fruit. Hairs are similar on the rest of the plant |
Note: All distances, elevations, and other facts are approximate. Names generally follow the USDA database.
![]() ; Last updated 240616
; Last updated 240616
| All Annual Forbs | Plant Species Index | Glossary | Copyright, Conditions, Disclaimer | Home |